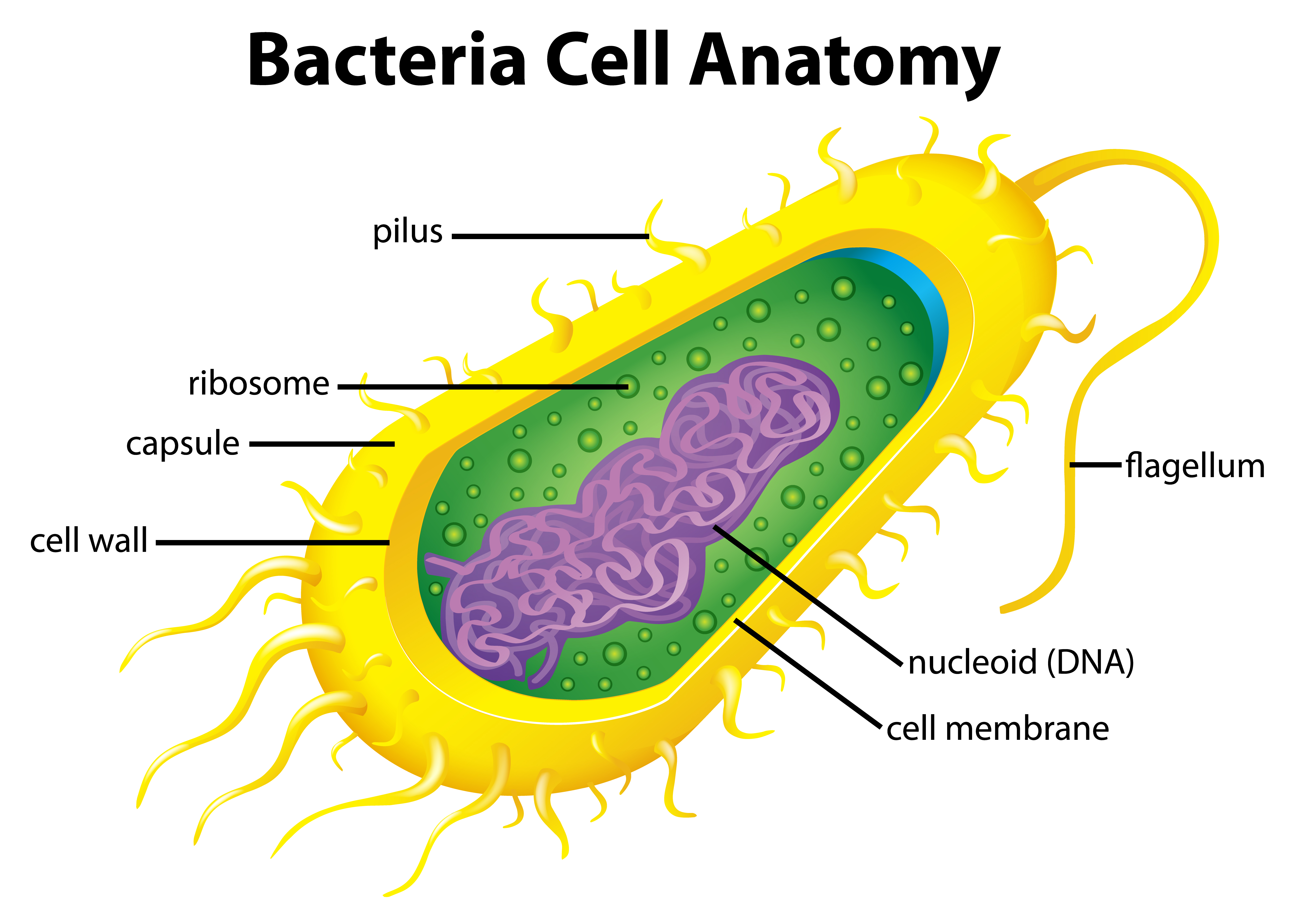
Bacteria Cell Vector Art, Icons, and Graphics for Free Download
Fungal and protistan cells also have cell walls. While the chief component of bacterial cell walls is peptidoglycan, the major organic molecule in the plant cell wall is cellulose (see structure below), a polysaccharide made up of glucose subunits. Figure 9. Cellulose is a long chain of β-glucose molecules connected by a 1-4 linkage.

5.E The Cell (Exercises) Biology LibreTexts
A bacterial cell (Fig. 2.5) shows a typical prokaryotic structure. The cytoplasm is enclosed by three layers, the outermost slime or capsule, the middle cell wall and inner cell membrane.
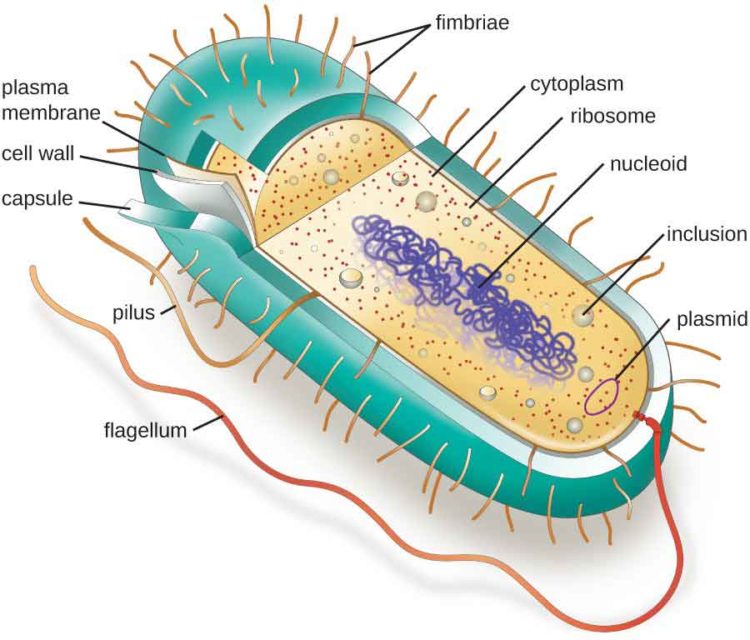
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
coccus (circle or spherical) bacillus (rod-like) coccobacillus (between a sphere and a rod) spiral (corkscrew-like) filamentous (elongated) Cell shape is generally characteristic of a given bacterial species, but can vary depending on growth conditions.
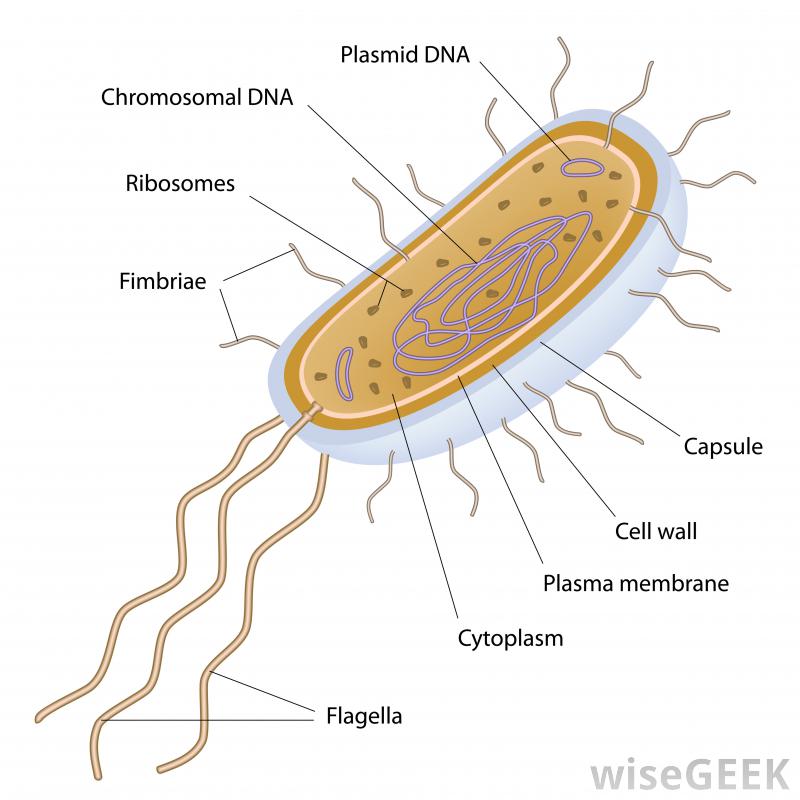
What part of the bacteria cell helps it stick to surfaces? Socratic
A prokaryote is a simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.

Bacterial Cell Diagrams 101 Diagrams
Bacteria are prokaryotes, lacking well-defined nuclei and membrane-bound organelles, and with chromosomes composed of a single closed DNA circle. They come in many shapes and sizes, from minute spheres, cylinders and spiral threads, to flagellated rods, and filamentous chains.
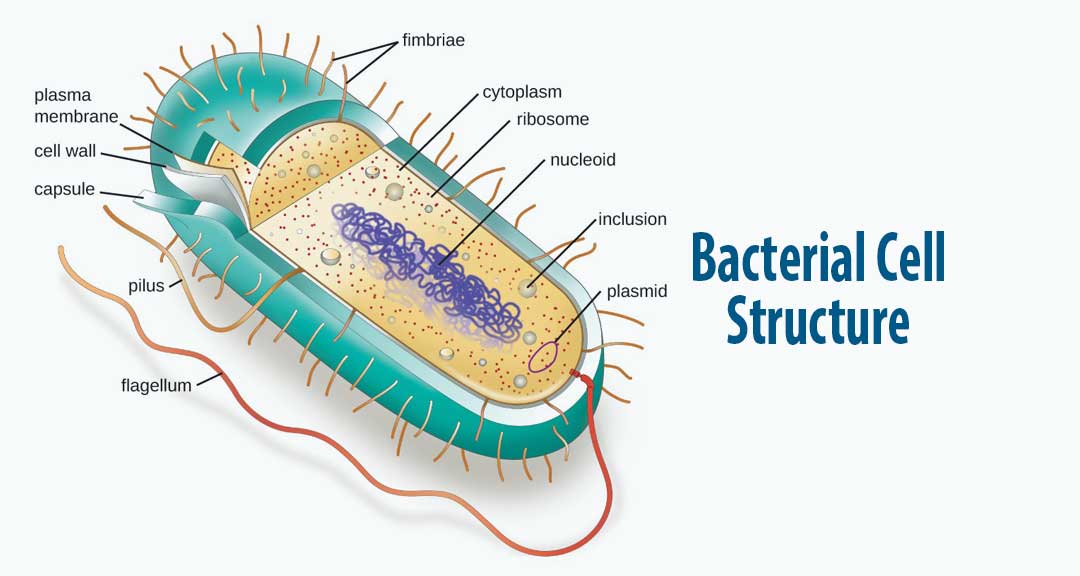
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function
Appendages which could be Pili or flagella Core components such as the cytosol, nucleoids, and plasmids Endospores - this consists of all bacteria cells components with dipicolinate and some special envelope components The structures listed above are not present in all types of bacteria.

Pin by Magpie on ชีวะ Prokaryotic cell, Eukaryotic cell, Prokaryotic cell model
Figure 1. Cutaway drawing of a typical bacterial cell illustrating structural components. See Table 2 below for chemical composition and function of the labeled components. Table 2. Summary of characteristics of typical bacterial cell structures. Structure. Flagella. Function (s) Swimming movement.
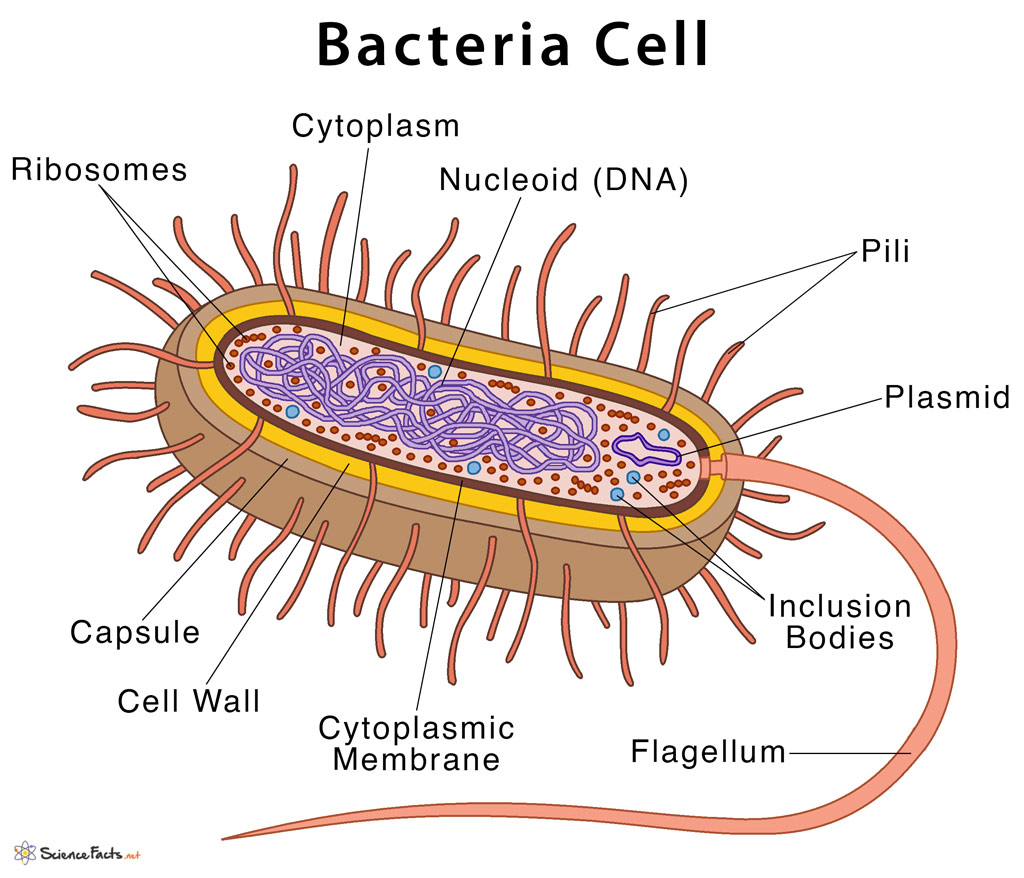
Characteristics of bacterial cells
Shape and Arrangement-1 Cocci (s., coccus) - spheres diplococci (s., diplococcus) - pairs streptococci - chains staphylococci - grape-like clusters tetrads - 4 cocci in a square sarcinae - cubic configuration of 8 cocci Shape and Arrangement-2 bacilli (s., bacillus) - rods coccobacilli - very short rods
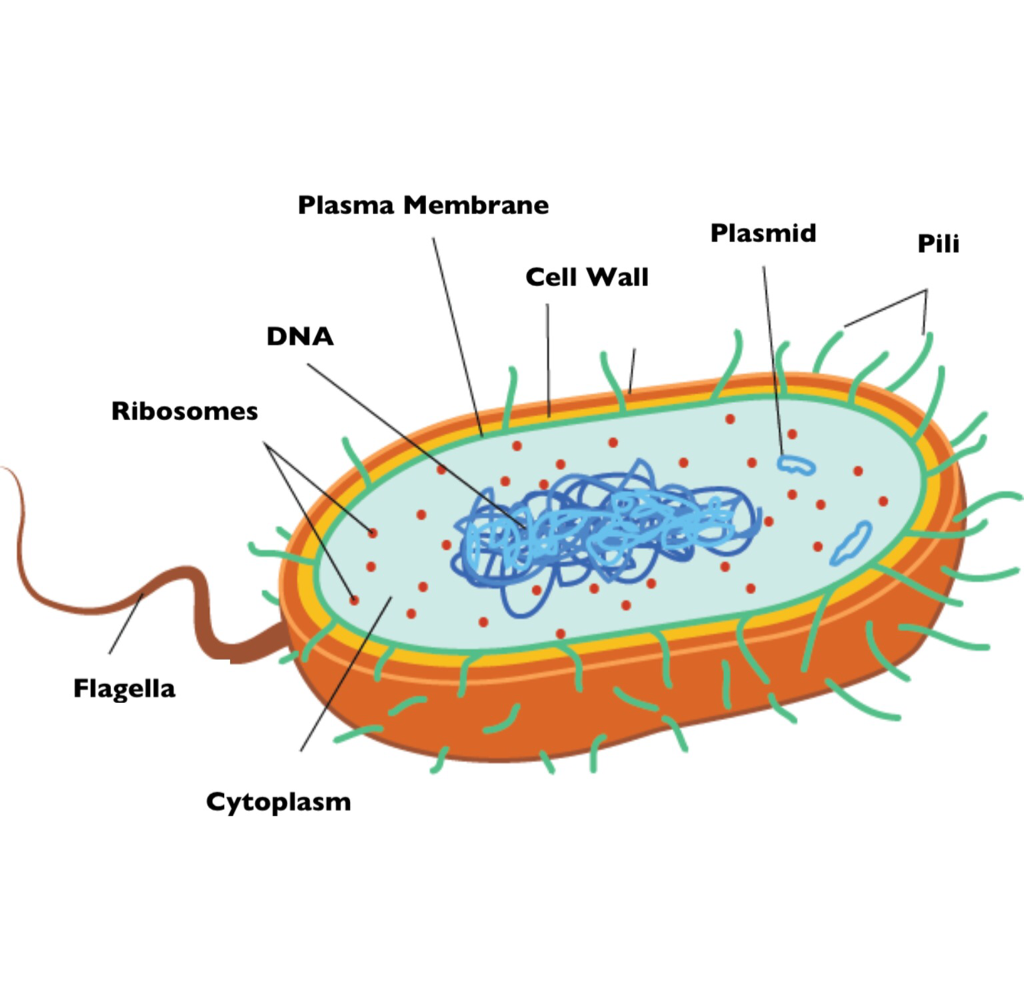
Bacteria Grade 11 Biology Study Guide
These can rotate or move in a whip-like motion to move the bacterium. Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection. Only plant cell walls are made from cellulose. The DNA of.
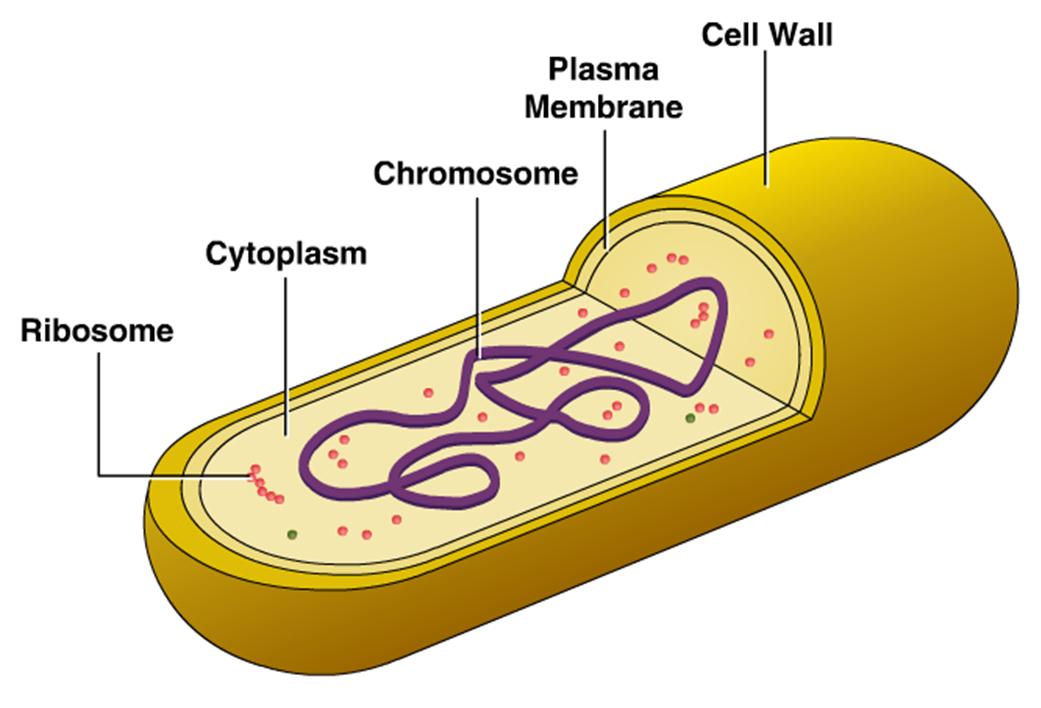
Innovic Medical Bacterial Cell Structure
bacteria, any of a group of microscopic single-celled organisms that live in enormous numbers in almost every environment on Earth, from deep-sea vents to deep below Earth's surface to the digestive tracts of humans. Bacteria lack a membrane-bound nucleus and other internal structures and are therefore ranked among the unicellular life-forms.
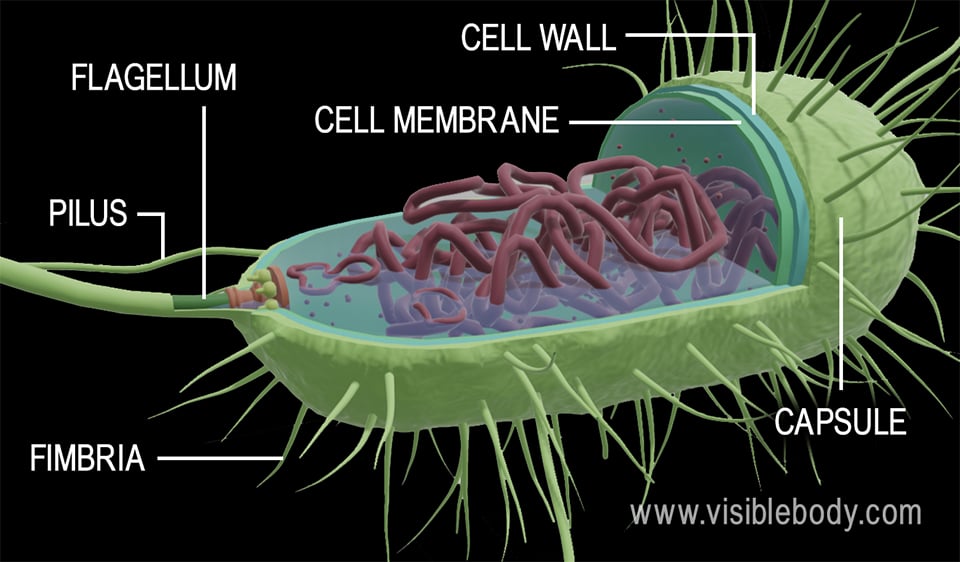
Bacteria Cell Structure
Definition Bacteria Diagram Ultrastructure of a Bacterial Cell Classification Reproduction Useful Bacteria Harmful Bacteria Today, bacteria are considered as one of the oldest forms of life on earth. Even though most bacteria make us ill, they have a long-term, mutual relationship with humans and are very much important for our survival.

Bacterial Structure Plantlet
Bacterial cells have simpler internal structures like Pilus (plural Pili), Cytoplasm, Ribosomes, Capsule, Cell Wall, Plasma membrane, Plasmid, Nucleoid, Flagellum, etc. Labeled Bacteria diagram Eukaryotes have been shown to be more recently evolved than prokaryotic microorganisms.
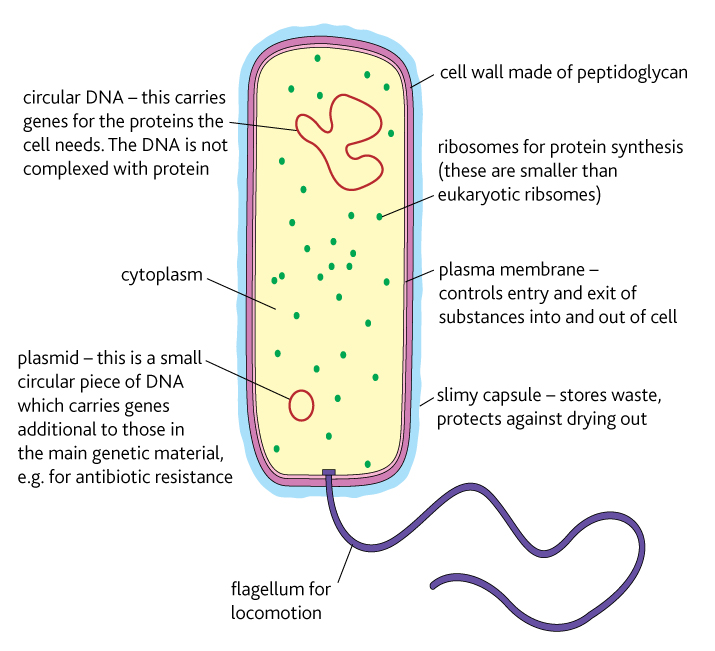
Bacterial cell structure Year 12 Human Biology
Capsule. A bacterial capsule is a polysaccharide layer that completely envelopes the cell. It is well organized and tightly packed, which explains its resistance to staining under the microscope. The capsule offers protection from a variety of different threats to the cell, such as desiccation, hydrophobic toxic materials (i.e. detergents), and bacterial viruses.

prokaryotic cell bacteria parts
Structure of Bacterial Cell (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: In this article we will discuss about the Structure of Bacterial Cell. Bacteria (sing. bacterium) are unicellular prokaryotic microorganisms which divide by binary fission.

Bacteria cell anatomy Royalty Free Vector Image
August 14, 2021. Bacteria are unicellular. Their structure is a very simple type. Bacteria are prokaryotes because they do not have a well-formed nucleus. A typical bacterial cell is structurally very similar to a plant cell. The cell structure of a bacterial cell consists of a complex membrane and membrane-bound protoplast.
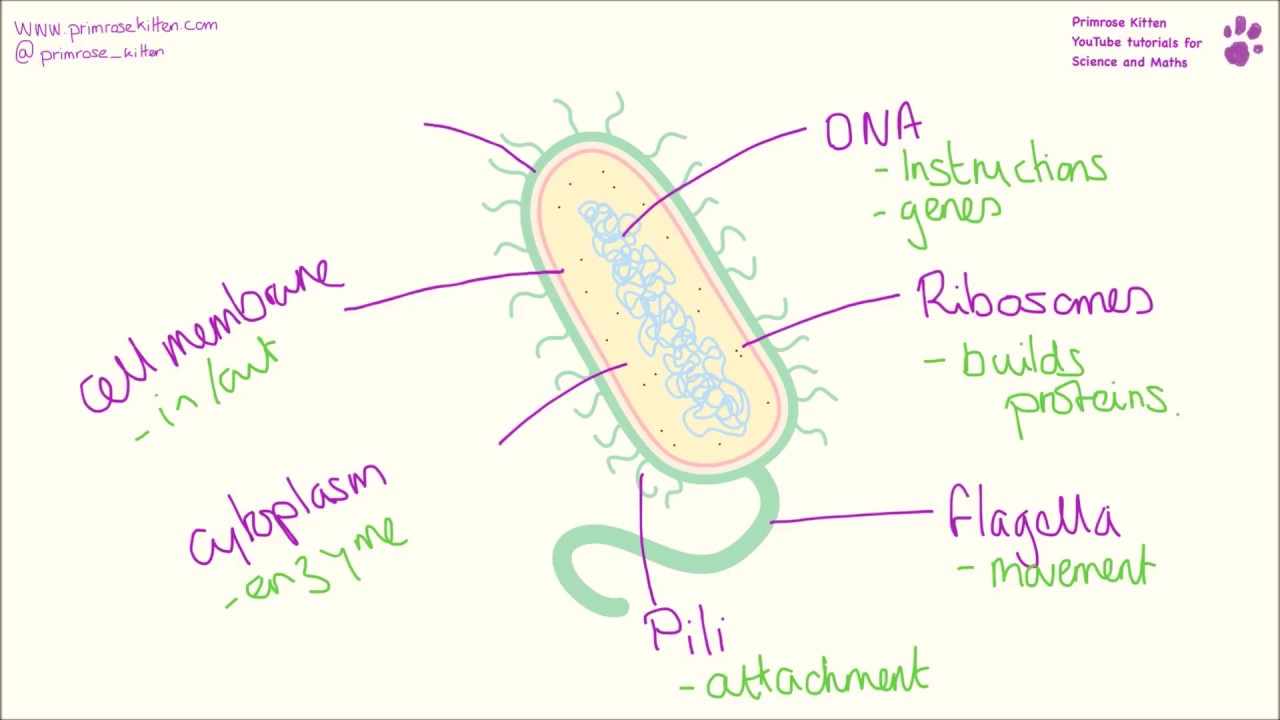
Bacterial cell structure and function YouTube
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms belonging to the domains Bacteria and Archaea. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells, have no nucleus, and lack organelles. All prokaryotic cells are encased by a cell wall. Many also have a capsule or slime layer made of polysaccharide.