
Nail Diagram Bing Images Biology Pinterest Nails, Search and The o'jays
In this video we discuss the structure of fingernails and toenails. We cover the different parts of nails and how nails grow. We also discuss some of the f.

FileHuman nail anatomy.jpg Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
A nail consists of: the nail plate, nail folds, nail matrix, nail bed and hyponychium. Nail plate. The nail plate is a rectangular and convex structure embedded within the nail folds. It originates from the nail matrices, found at the base of the nails. The nail plate is completely free distally to the onychodermal band (distal margin of the.

diagram of nail anatomy
Overview. The nail organ is an integral component of the digital tip. It is a highly versatile tool that protects the fingertip, contributes to tactile sensation by acting as a counterforce to the fingertip pad, and aids in peripheral thermoregulation via glomus bodies in the nail bed and matrix. [ 1, 2] Because of its form and functionality.

Fingernails Ingrown fingernails Dark Line Fingernail Pain
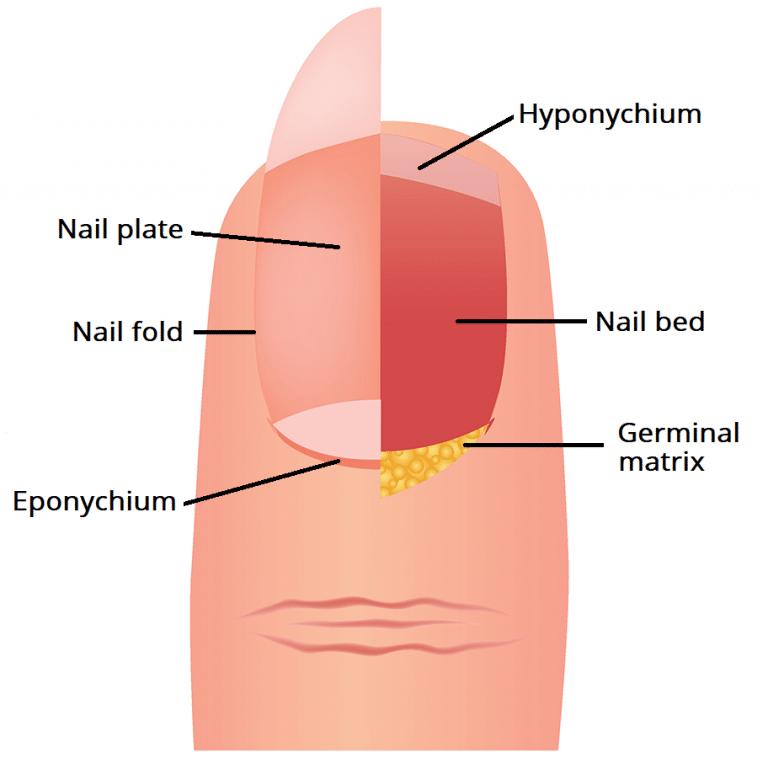
The nail unit is a complex structure located on the dorsal surface of the fingers and toes. It has two main functions: Protection - protects the digits from trauma Sensation - assists with tactile sensation In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the nail unit - its component parts and clinical correlations.
Nail Anatomy
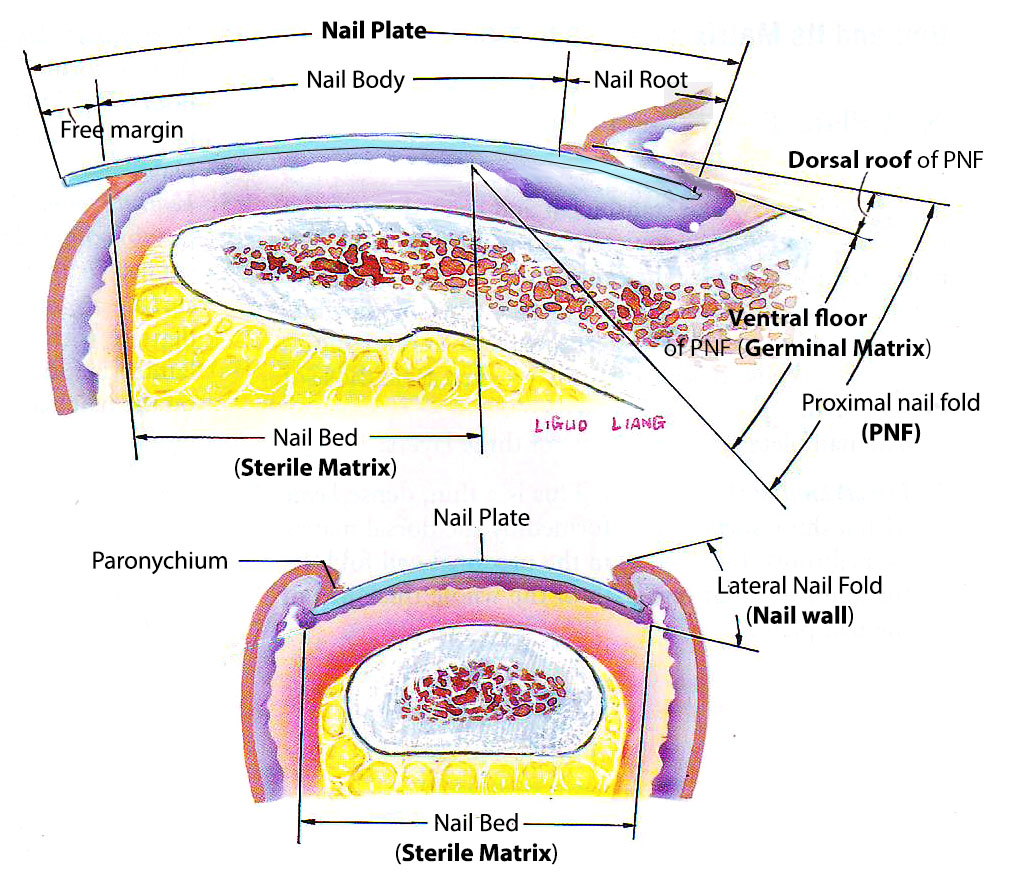
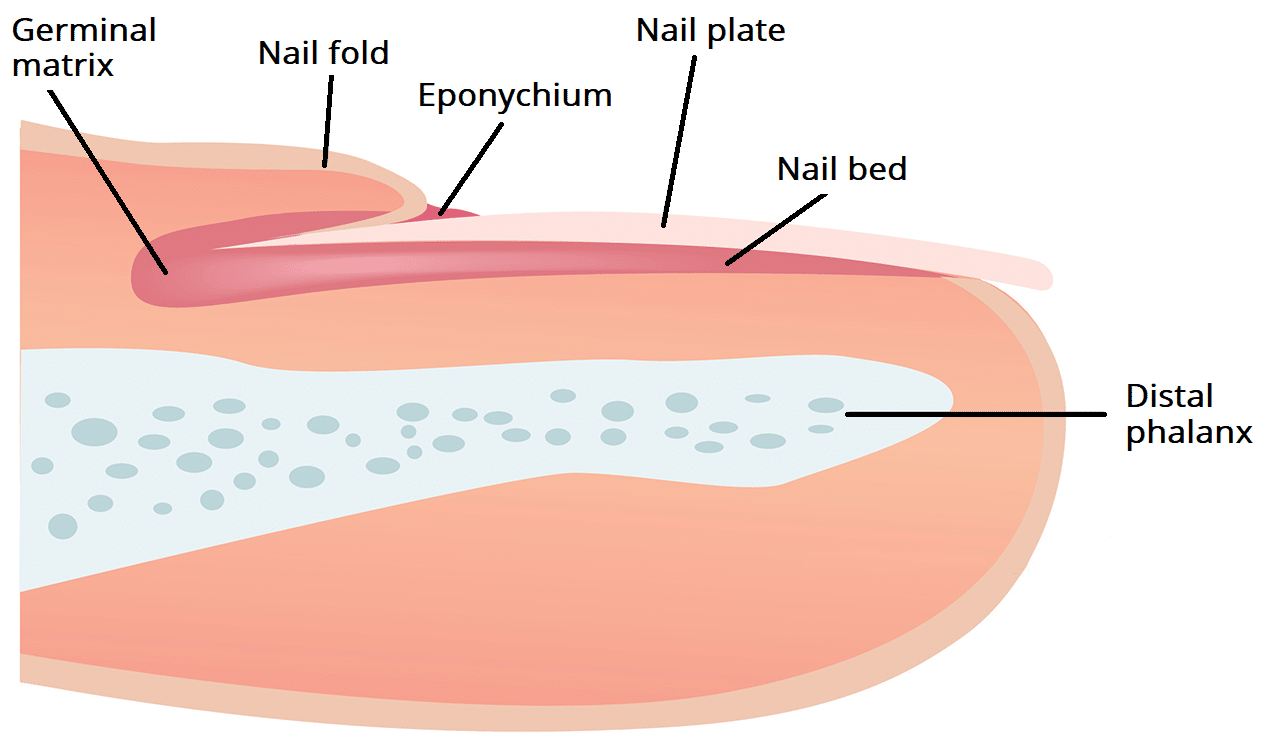
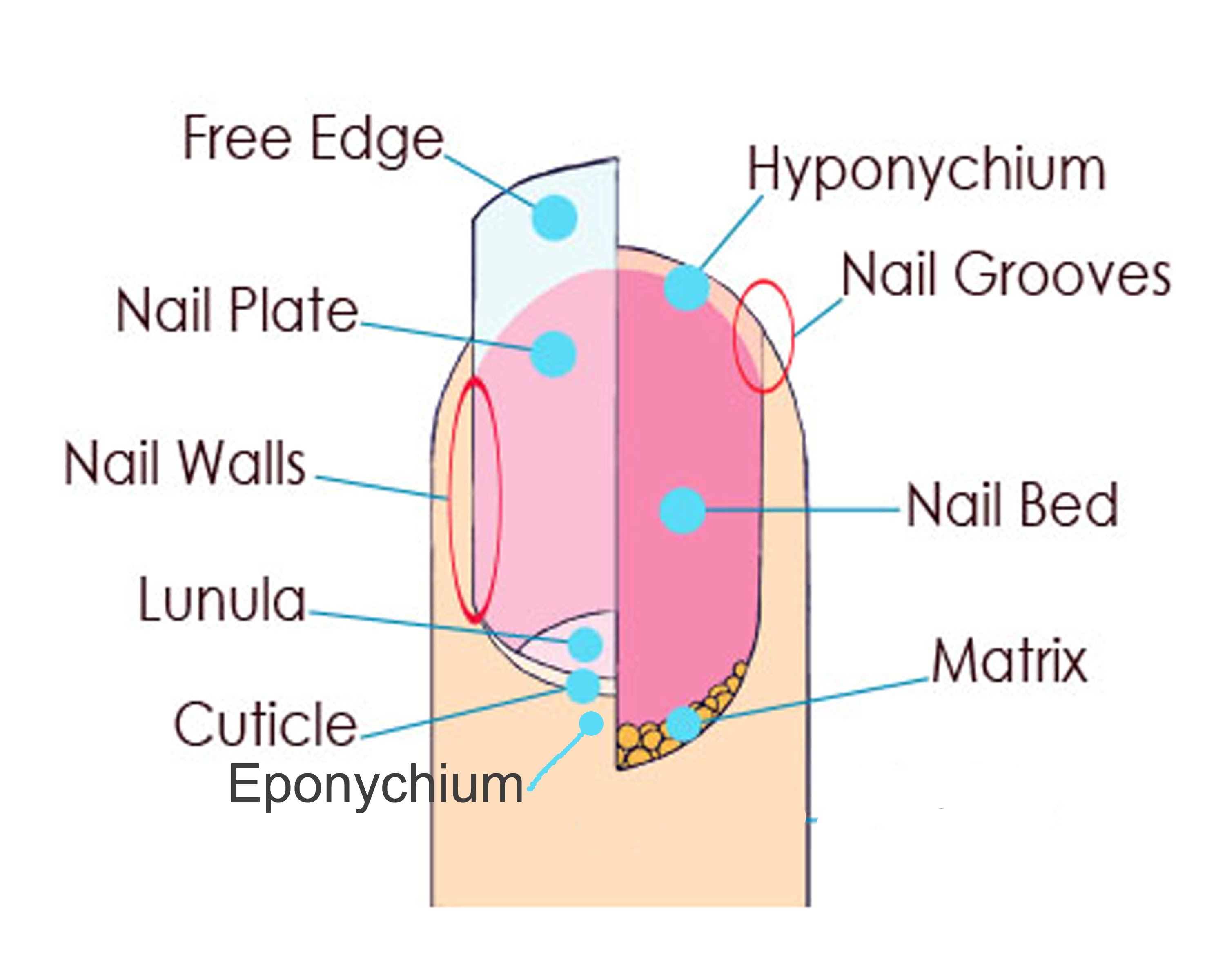
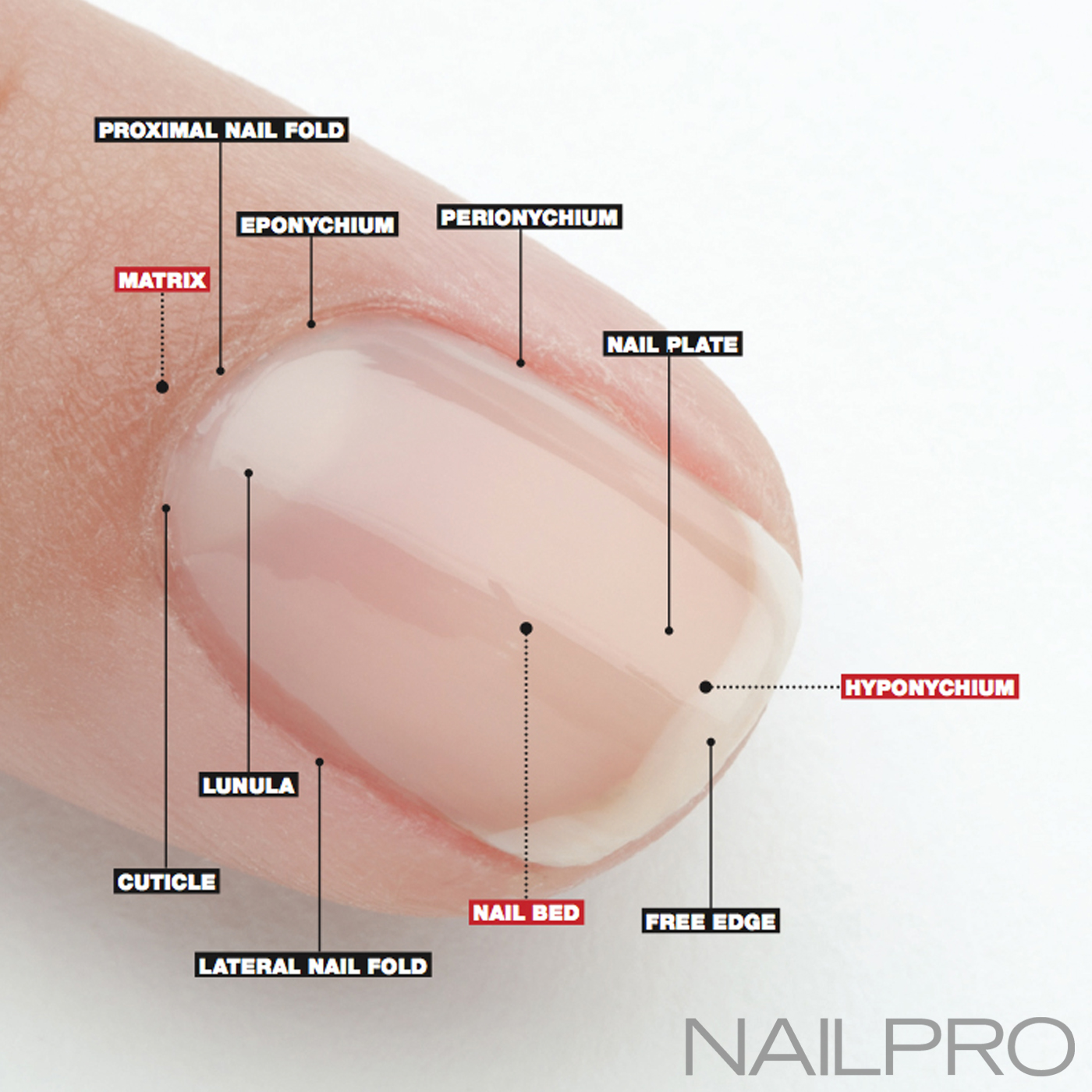
Underlying Structures The nail bed is also referred to as the sterile matrix. It extends from the edge of the nail root, or lunula, to the tissue known as hyponychium . The nail bed contains blood vessels, nerves, and melanocytes that produce melanin.
Nail Germinal Matrix Histology nailsr
Structure of the nails Created: June 28, 2018; Next update: 2021. Fingernails and toenails are made from skin cells. Structures that are made from skin cells are called skin appendages. Hairs are also skin appendages. The part that we call the nail is technically known as the "nail plate."

Healthy nail with normal anatomic structures in place. (A) Surface... Download Scientific Diagram
The nail plate consists of close-packed, adherent, interdigitating cells that lack nuclei or organelles. Cells in the plate are very flat, lying with the smallest diameter perpendicular to the plane of the nail plate surface ( Fig. 5.5).There is a progression from the top (dorsal surface) of the plate, where cell borders are straight, to the middle of the plate, where cell borders are much.

A longitudinal section showing the structure of a nail. Longitudinal section, Nursing school
Dec. 29, 2023, 9:08 PM ET (Yahoo News) Hanceville council back at business in wake of Nail resignation nail, in the anatomy of humans and other primates, horny plate that grows on the back of each finger and toe at its outer end. It corresponds to the claw, hoof, or talon of other vertebrates.

Fingernail/ظفر/指甲(Zhǐjiǎ) Step by step into english in English
Anatomy of the Nails. The nail bed is a specialized structure of the epidermis that is found at the tips of our fingers and toes.. Above: Illustrated diagram of the anatomy of a fingernail. Above: Microscopic images of a fingernail cross section. The top image is magnified by 4x and the bottom image is the same tissue sample as the top image.
Manicure The Ontario Nail Institute
Structure A. Nail plate; B. lunula; C. root; D. sinus; E. matrix; F. nail bed; G. hyponychium; H. free margin. The nail consists of the nail plate, the nail matrix and the nail bed below it, and the grooves surrounding it. [2] Parts of the nail The nail matrix is the active tissue (or germinal matrix) that generates cells.
Nail Anatomy A Professional Primer on the Parts of the Nail
Nail Plate - This is the thing most people refer to as the fingernail. The largest part of the nail is composed of layers of keratin. The structure is similar to human skin and hair since it is.

13 best images about Chapter 8 Structure of the Nails on Pinterest Nail strengthening
Here, a refresher on the essential parts of the nail, from base to tip and everything in between. Located beneath the skin at the nail's base, the matrix contains nerves and blood and lymph vessels that produce nail cells. The new cells flatten and are pushed forward toward the fingertip resulting in nail growth.

PPT Unit 4 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2098133
Nail Anatomy. Figure 10.6.2 The top diagram in this diagram shows the external, visible part of the nail and the cuticle. The bottom diagram shows internal structures in a cross-section of the nail and nail bed. A nail has three main parts: the root, plate, and free margin. Other structures around or under the nail include the nail bed, cuticle.

Structure of a Nail (CrossSectional View) Diagram Quizlet
Figure 1. The nail is an accessory structure of the integumentary system. In addition, the nail body forms a back-support for picking up small objects with the fingers. The nail body is composed of densely packed dead keratinocytes. The epidermis in this part of the body has evolved a specialized structure upon which nails can form.
The Nail Unit Plate Germinal Matrix Bed TeachMeAnatomy
Structure. The nail unit includes the nail plate and supporting structures. This section explains the anatomy of the nail unit and histologic findings of each region.. Ink, suture, or an accompanying diagram can facilitate communication of the orientation. Processing a nail biopsy is more challenging than a standard skin biopsy. The specimen.
6.4 Anatomy of the Nails Biology LibreTexts
Toenails A nail is a horn-like envelope covering the dorsal aspect of the terminal phalanges of fingers and toes in humans, most primates, and a few other mammals. Nails are similar to claws, which are found on numerous other animals. In common usage, the word nail often refers to the nail plate only.